3.2 How does tobacco use affect schizophrenia?
Although smoking may appear to offer temporary relief, it can impact emotions and behavior, complicating the management of schizophrenia.

3.2 How does tobacco use affect schizophrenia?
Although smoking may appear to offer temporary relief, it can impact emotions and behavior, complicating the management of schizophrenia.
‘The momentary ease nicotine can bring often hides the truth that it’s fueling the addiction, complicating efforts to quit.’
Understanding how nicotine affects the brain in schizophrenia can help to determine whether it truly helps or harms.
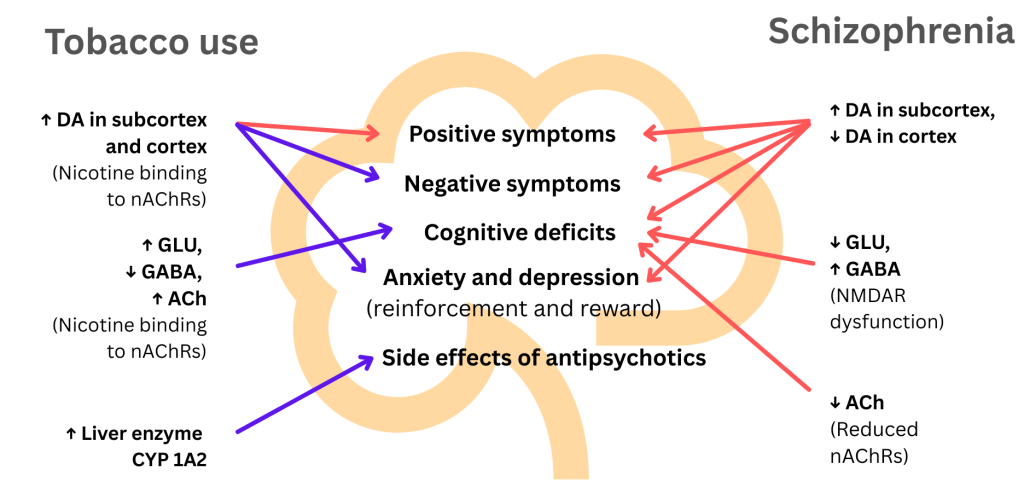
How tobacco use affects the brain in schizophrenia

Quitting matters!
While some studies suggest that smoking may help alleviate the symptoms of schizophrenia and improve cognitive functions like attention and memory, these potential benefits are overshadowed by the significant negative impact of tobacco use, making the management of schizophrenia even more challenging.
Smoking in people with schizophrenia has been associated with:
increased anxiety, agitation,
and worsening symptoms of psychosis, like hallucinations or delusions,
as well as reduced cognitive abilities.
Furthermore, smoking has been linked to higher rates of suicidal behavior among those with schizophrenia.
On the flip side, quitting tobacco has been shown to improve both mental clarity and psychosis symptoms, as well as lower the risk of other health problems.
Despite these benefits, people with schizophrenia often receive less support to quit smoking compared to those without the condition.
The true cost of smoking for people with schizophrenia
Aside from the health risks associated with tobacco use, there are additional challenges for people with mental disorders:
• Financially, spending on tobacco can be a significant portion of their income,
• Socially, tobacco use can also increase discrimination and stigma in their lives.
These factors compound the difficulties faced by individuals with mental health conditions who smoke.
Financial impact of tobacco use in schizophrenia
Tobacco smoking isn’t just a health issue for people with schizophrenia – it also has serious financial consequences.
A study in the U.S. found that individuals with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder who rely on public assistance spend nearly 27% of their monthly funds on cigarettes.
This shows just how much of a financial burden smoking can be for those already facing significant challenges.
Social impact of Tobacco Use Disorder in schizophrenia
Stigma and discrimination significantly impact people dealing with tobacco use disorder and schizophrenia.
Even though modern neuroscience and psychiatry reveal that these conditions are linked to structural and functional brain problems, many still view TUD as rather a result of poor decisions or bad behavior than a true medical condition. This misconception lowers effective prevention and treatment.
Overcoming stigma is essential to ensure the patient receives the right care and support.