Why is treatment adherence so vital?
Effective treatment for dual schizophrenia must address biological, psychological, and social factors, with antipsychotic medication playing a central role.
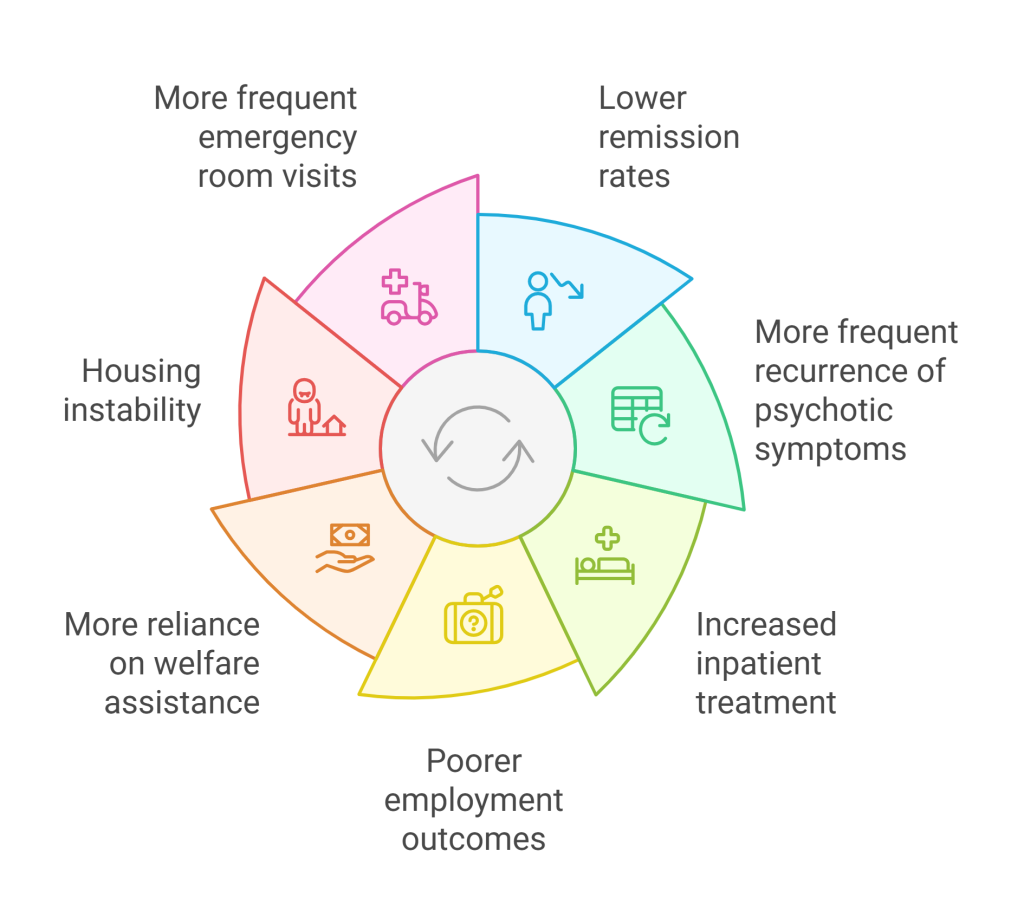
Staying on track with medication – taking the right dose at the right time – is essential for managing symptoms, preventing relapses, and improving life expectancy. On the contrary, poor adherence, such as missing doses, taking incorrect amounts, or stopping medication without medical guidance, can weaken treatment effectiveness and increase the risk of relapse.
Relapse is a major concern, especially since experiencing one makes future relapses more likely. Medication nonadherence is a key predictor of relapse, particularly the first one.
Other factors, such as coexisting medical or psychiatric conditions and substance use disorders, can also contribute to relapse by either disrupting medication routines or worsening symptoms.
The type of care provided plays a critical role in long-term stability.
For individuals with dual schizophrenia, treatment must target both schizophrenia symptoms and those related to substance use disorder.
Tailoring therapy to each patient’s unique needs increases the likelihood of adherence, leading to better outcomes and improved overall well-being.